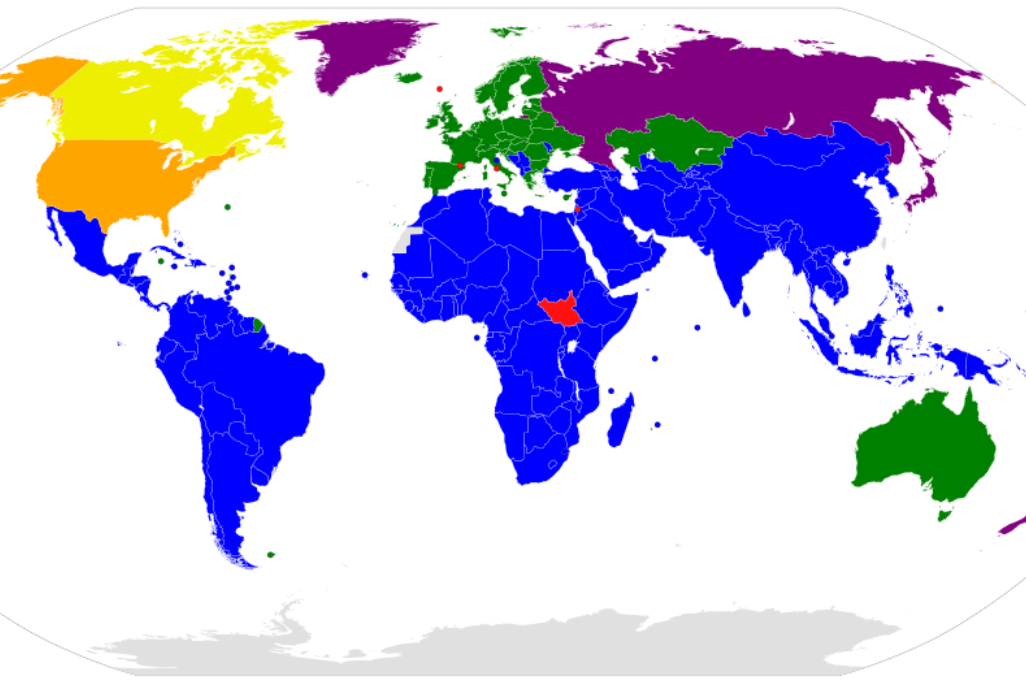
The Cartagena Protocol of the convention on biological diversity
The Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety is an international treaty under the Convention on Biological Diversity. It addresses the safe transfer, handling, and use of living modified organisms (LMOs) resulting from modern biotechnology, to ensure the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity. The protocol promotes information sharing and risk assessment, aiming to minimize potential adverse effects on the environment and human health. It came into effect in 2003 and has been ratified by numerous countries to establish guidelines for the responsible use of biotechnology and genetically modified organisms. The conclusion of the Biosafety Protocol has been hailed as a significant step.
Forward in that it provides an international regulatory framework to reconcile the
respective needs of trade and environmental protection with respect to a rapidly
growing global industry, the biotechnology industry. The Protocol thus creates
an enabling environment for the environmentally sound application of
biotechnology, making it possible to derive maximum benefit from the potential
that biotechnology has to offer, while minimizing the possible risks to the
environment and to human health.