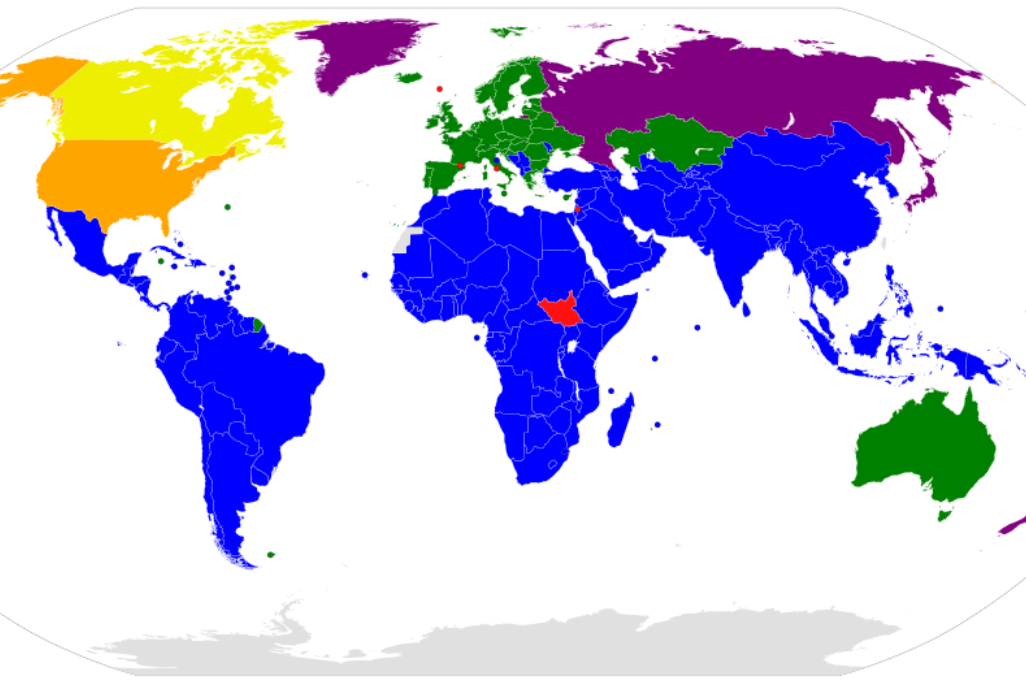
Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The Kyoto Protocol is an international treaty linked to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). It was adopted in 1997 and came into force in 2005. The protocol aimed to address global climate change by setting legally binding emission reduction targets for developed countries. These targets were collectively known as “quantified emission limitation and reduction commitments.” The protocol established three flexible mechanisms—Clean Development Mechanism, Joint Implementation, and Emissions Trading—to help countries meet their targets more cost-effectively. However, the Kyoto Protocol had limitations, and its effectiveness was debated. It was succeeded by the Paris Agreement in 2015, which aimed to involve all countries, both developed and developing, in tackling climate change.







